Liver cancer is one of the cancers that sees a fast increasing rate of occurrence in India. Primary and secondary liver tumours have been a global health problem for a long time. In India, recent data suggests that about 30,000 to 50,000 new cases of liver cancer are being identified every year.
Treatments for liver cancer
The treatment for liver cancer depends on the extent of the progression of the disease, along with taking in factors like the patient’s age, health, and preferences.
1. Surgery
If the liver cancer is at an early stage, with the rest of the liver remaining healthy, surgery (partial hepatectomy) might be recommended. The tumour should be small with the blood vessels free of infection for the surgery to be suggested.
2. Liver transplantation
Another option that is recommended for people with early-stage liver cancer is liver transplantation. However, liver transplantation is usually recommended only for a small group of people with early-stage liver cancers.
Here are some of the cases in which liver transplantation is recommended.
● When the cancer is at the early stage, but the rest of the liver isn’t in a healthy condition.
● The tumour is present in a risky spot to operate (Near a blood vessel).
A patient will have to wait until the liver is available for the liver transplant. During this waiting period, other treatments like ablation and embolization are given to the patient so that the cancer is under control.
About 20,000 people require liver transplantation in India every year, but only about 800-900 surgeries are performed every year. Only a limited number of liver transplantation hospitals in India have the right equipment and specialists to perform the transplantation surgery.
3. Minimally invasive procedures
There are some cases where these conventional treatments fail to produce the required results, and the patient might not be complying with the surgery, or the transplant might not be available. In these cases, minimally invasive treatments are recommended to treat liver cancer. There are various minimally invasive interventional treatments available like laparoscopic liver resection (LLR), Microwave ablation (MWA), radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and more. Depending on cancer and other factors, your doctor might recommend a particular procedure. Here are some of these minimally invasive procedures explained.
Trans Arterial Chemo Embolization
Trans Arterial Chemo Embolization, also known as TACE,is a minimally invasive procedure that is usually used to treat hepatocellular carcinoma. TACE is considered an evolution from a previously used method called Trans-catheter Arterial Embolization (TAE).
TACE involves a two-step process. Selective arterial occlusion limits the blood supply to the tumour, which induces ischemic tumour necrosis. Then regional chemotherapy is provided with helps the drug to remain in the area for an extended period which starts causing the therapeutic effects. TACE makes it possible to selectively embolize the hepatic artery branches while leaving out the healthy hepatic tissues.
TACE is recommended for patients with asymptomatic and unresectable liver cancers. TACE can be used to reduce the size of the tumour and make the patient eligible for resection or liver transplantation.
Radiofrequency ablation
Tumour ablation techniques involve administering chemicals or energy to the target tissue through needle-like devices. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is used to treat HCC and metastatic colorectal carcinoma in the liver, and it has been proven effective in treating tumours less than 3cm in size.
Other than RFA, there are other ablation techniques like Microwave ablation, Cryoablation and more.
We recently performed superselective Trans Arterial Chemo Embolization (TACE) for liver cancer. The patient was an elderly lady who had inoperable liver cancer. Using microcatheters (less than a millimeter diameter), we reached the arteries supplying the cancer. The skin incision in the groin was less than 3 mm in size and no sutures were required. The chemotherapy agent(to kill cancer cells) was injected directly into the arteries supplying the cancer. By this method, the general side effects seen with systemic chemotherapy will be markedly reduced. After the procedure, the patient needs to stay for a day or two for observation and can go back home. Regular monitoring of the cancer by CT scan is required to monitor shrinkage of the cancer.
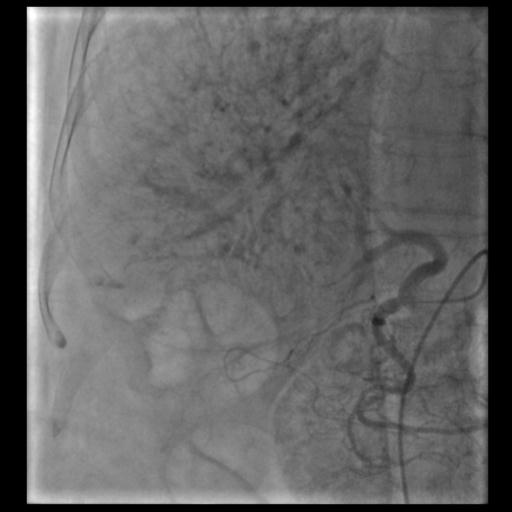 |
| Hepatic Angiogram showing tumour vascularity |
 |
| Selective chemo embolisation of tumour feeders |
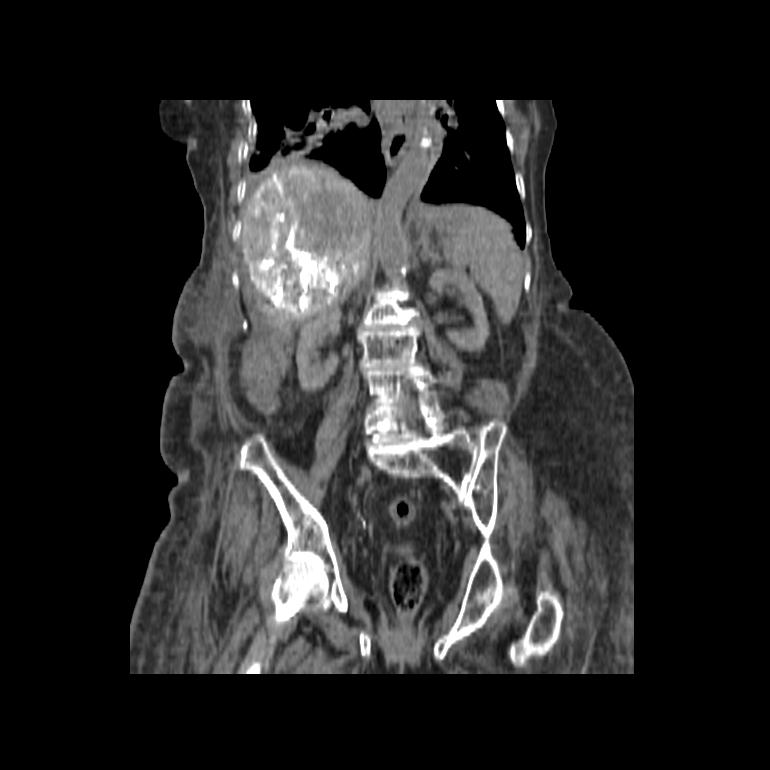 |
| Post treatment CT showing selective uptake of agent within the tumour |
Kauvery Hospital is globally known for its multidisciplinary services at all its Centers of Excellence, and for its comprehensive, Avant-Grade technology, especially in diagnostics and remedial care in heart diseases, transplantation, vascular and neurosciences medicine. Located in the heart of Trichy (Tennur, Royal Road and Alexandria Road (Cantonment), Chennai, Hosur, Salem, Tirunelveli and Bengaluru, the hospital also renders adult and pediatric trauma care.
Chennai – 044 4000 6000 • Trichy – Cantonment – 0431 4077777 • Trichy – Heartcity – 0431 4003500 • Trichy – Tennur – 0431 4022555 • Hosur – 04344 272727 • Salem – 0427 2677777 • Tirunelveli – 0462 4006000 • Bengaluru – 080 6801 6801



