Table of Content
The brain is one of the most important organs of the body and needs plenty of oxygen-rich blood for its proper functioning. This is provided by four primary arteries and a vast network of capillaries and blood vessels inside the brain. A pair of vertebral arteries run through the spine and supply blood to the back part of the brain. A pair of carotid arteries, located in the neck, one on either side of the head, supply blood to the front part of the brain which is larger. It is also an important part of the brain as it is responsible for sensory functions, motor functions, thinking, speech and personality.
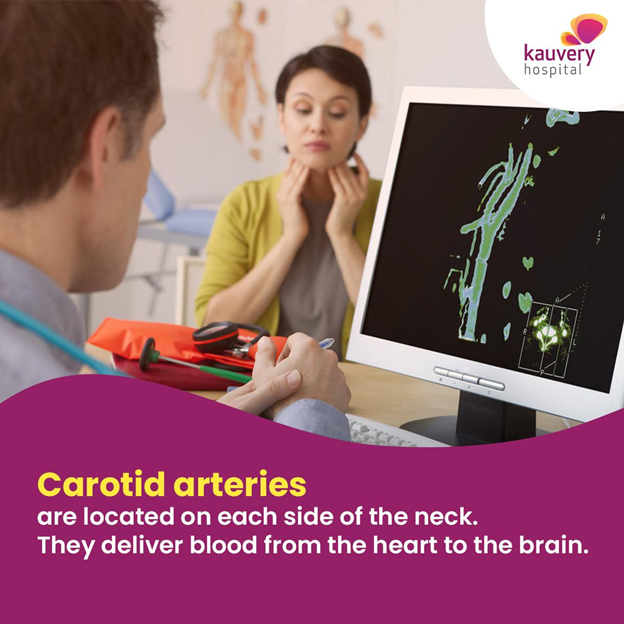
Similar to coronary arteries of the heart, the carotid arteries can also develop a blockage due to plaque deposits, a condition called atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis causes narrowing down of the arteries, which is why the condition is called carotid artery stenosis.
Consequences and complications
The most prominent outcome of atherosclerosis in the carotid arteries is ‘stroke’ technically called a transient ischemic attack or TIA. As the name implies, the blood supply to one or more parts of the brain gets disrupted causing cessation of activity in one or more areas. There are four different ways in which a stroke is triggered.
- The carotid artery(ies) get narrowed down significantly, which greatly reduces the blood flow to many parts of the brain.
- Atherosclerosis increases blood pressure which over time weakens the artery. A weakened carotid artery can rupture and hemorrhage blood instead of supplying to the brain.
- A piece of plaque breaks off from a spot of build-up and travels to the smaller arteries of the brain where it gets stuck and disrupts blood flow.
- The body recognizes the piece of plaque as an injury and starts clotting the blood. A blood clot can lodge in the carotid artery or any of the capillaries downstream, thereby obstructing blood flow.
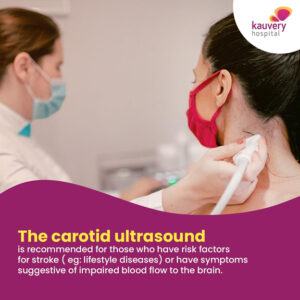
Risk Factors for blockage in Carotid arteries
- Hypertension: High blood-pressure puts pressure on the arterial walls, weakening them and increasing the risk of a rupture.
- Tobacco use and abuse; Smoking increases heart rate and blood pressure. Further Nicotine can irritate the inner lining of arteries.
- Diabetes lowers the body’s ability to process fat efficiently, which increases the risk of hypertension and atherosclerosis.
- High blood-fat levels: High levels of LDL (bad cholesterol) and triglycerides increase the risk of plaque formation.
- Genes: A family history of atherosclerosis increases your own risk
- With age, arteries become stiff and vulnerable to injury
- Obesity: Excess weight creates a vicious circle of diabetes, high BP and atherosclerosis
- Sleep apnea: Disruption in breathing during sleep increases the risk of stroke.
- Lack of exercise: A sedentary lifestyle can eventually trigger high BP, diabetes and obesity
- Insulin resistance and Diabetes
Signs and Symptoms of blocked Carotid Artery
Just for you to be aware, strokes can be caused by many reasons other than carotid artery stenosis. But when it comes to symptoms, for all practical purposes, symptoms of carotid artery stenosis are same as that of a stroke. This includes:
- Sudden numbness, weakness or tingling in the face, hands or legs, on only one side of the body
- Sudden trouble in speaking (slurred speech) or understanding what the other person is saying
- Sudden loss of vision or blurred vision in one or both eyes
- Sudden dizziness and/or confusion
- Sudden and severe headache
- Sudden loss of balance, lack of coordination and difficulty in walking
- Aphasia or sudden difficulty in speaking
- Sudden difficulty in remembering simple information (memory issues)
- Dysphagia or sudden difficulty in swallowing
- Drooping on one side of the face
Diagnosis
Various tests are conducted to confirm (or rule out) the condition, and its severity.
- Physical exam: The doctor uses a stethoscope to listen to an abnormal sound (called bruit – ‘bro-ee’) in the carotid artery.
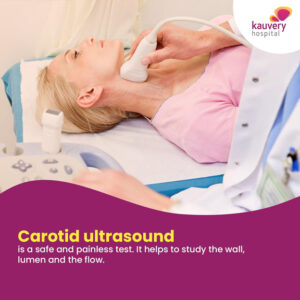
- Carotid ultrasound: A standard or Doppler ultrasound that uses ultrasound waves to get a clear picture of the carotid artery and blood flow in the same.
- CT scan: A CT scan of the brain produces 3D pictures of the arteries there, on a large computer screen.
- CT angiogram: Here, a mildly radioactive dye is injected into the artery and CT scan done thereafter. This will show the blood flow and blockage if any
- MR angiogram: Here, a magnetic field along with radio waves are used to create a picture of the carotid artery
- Carotid angiogram: Similar to angiogram done for the coronary arteries: Here, a catheter is inserted into a hole made in the groin or arm and threaded all the way to the carotid artery using a special X-ray machine, Contrast dye is injected into the carotid artery using the catheter and sophisticated images of the arteries are produced.
Treatment for Carotid Arteries

Three primary options for treatment are available and the doctor will decide if one or more of these must be employed and if so, when.
- Lifestyle changes: The doctor will recommend reducing weight, salt intake, sugar intake and alcohol consumption. He/she will advise the patient to quit smoking, exercise more and consume a healthy diet low in fatty or refined foods and high in fresh fruits and vegetables. Along with a nutritionist, and therapist, he/she may design a diet plan and fitness program.
- Medication: Medicines are given to reduce the risk of all those conditions which encourage plaque formation or atherosclerosis. This includes medicines to keep diabetes under check, reduce BP and cholesterol. Anti-platelet medication and blood-thinners which help reduce the risk of blood clot formation, are also given.
- Surgical procedures: When the above treatment options are not enough, as seen by diagnostic tests, the doctor may undertake one of these:
- Carotid Endarterectomy: This is an incisional surgery where, the doctor will make a cut in the neck to access the carotid artery at the spot of blockage, cut the artery, clean out the plaque and then suture it again. Suitability and results vary from person to person.
- Carotid Artery stenting: Exactly similar to coronary artery stenting. A catheter fitted with an inflatable balloon is inserted into the body and threaded all the way to the spot of the blockage in the carotid artery. The balloon is inflated which pushes the plaque deposits against the arterial wall, while a metal coil called the stent is left behind after the balloon is deflated. This ensures the artery which has been widened now stays wide.
Outlook
The worst part of Carotid Artery Stenosis is that there are no symptoms until an actual stroke occurs. The transient attack of a mini-stroke is a warning sign that something is wrong. But waiting until a stroke occurs is risky, as complications can arise later. That is why it’s important for all adults above 30 years of age to have a comprehensive health checkup once a year, and for adults above 60 years of age – twice a year. These tests can highlight several red flags concerning your health. Specialists, such as our heart doctors in Salem, Trichy, Hosur, Tirunelveli or Chennai, can then advise you on the risks you face and recommend preventive measures to reduce the risk of conditions like Carotid Artery Stenosis. Consulting a reputed hospital for these check-ups is advisable, as both diagnosis and consultation will be available under one roof.
Kauvery Hospital is globally known for its multidisciplinary services at all its Centers of Excellence, and for its comprehensive, Avant-Grade technology, especially in diagnostics and remedial care in heart diseases, transplantation, vascular and neurosciences medicine. Located in the heart of Trichy (Tennur, Royal Road and Alexandria Road (Cantonment), Chennai, Hosur, Salem, Tirunelveli and Bengaluru, the hospital also renders adult and pediatric trauma care.
Chennai – 044 4000 6000 • Trichy – Cantonment – 0431 4077777 • Trichy – Heartcity – 0431 4003500 • Trichy – Tennur – 0431 4022555 • Hosur – 04344 272727 • Salem – 0427 2677777 • Tirunelveli – 0462 4006000 • Bengaluru – 080 6801 6801



